Biochar has emerged as a game-changer in sustainable agriculture and gardening, thanks to its unique characteristics and benefits. Derived from the pyrolysis of organic materials, biochar is a stable, carbon-rich product that can greatly enhance soil health. This article explores the differences between raw biochar and inoculated biochar, and the benefits of each for your soil management practices.
Characteristics of Biochar
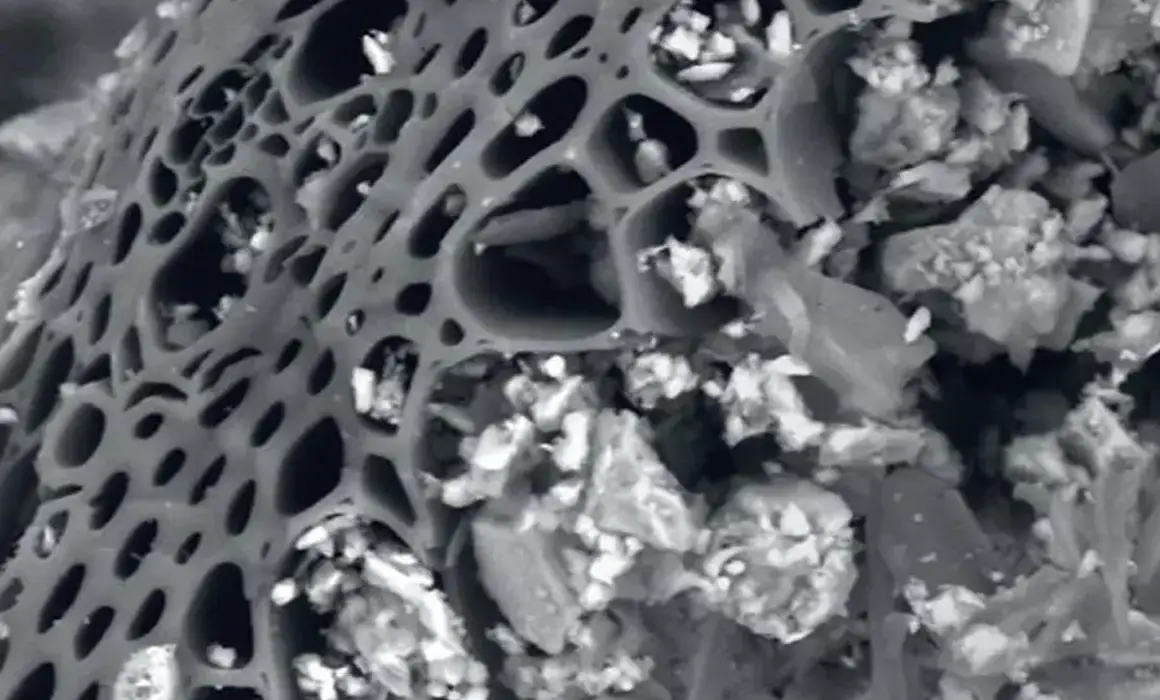
Biochar is created by heating organic materials in an oxygen-limited environment at high temperatures, a process called pyrolysis. This results in a stable, carbon-rich material that retains over 80% of the original carbon from the biomass. Biochar’s porous structure allows it to retain water, nutrients, and support beneficial soil microbes, making it an ideal soil amendment.
Key Benefits of Biochar for Soil Health
Biochar is more than just a carbon-rich supplement; its unique physical and chemical properties make it a versatile addition to soil management strategies.
- High Surface Area: Biochar has a porous structure, providing a significant surface area that can retain water, nutrients, and nurture soil microbes. This structure improves soil aeration and moisture retention.
- Stability: Biochar is resistant to decomposition, allowing it to sequester carbon in the soil for hundreds to thousands of years. This stability makes it an effective tool for carbon sequestration and combating climate change.
- Nutrient Retention: Biochar has a cation exchange capacity (CEC) that allows it to hold positively charged nutrients, like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, preventing them from leaching away during rainfall or irrigation.
- pH Buffering: Depending on the feedstock and pyrolysis conditions, biochar can help regulate soil pH, making it less acidic and more suitable for plant growth. This buffering capacity is particularly beneficial in areas with naturally low soil pH.
- Microbial Habitat: The porous structure of biochar provides an excellent habitat for microorganisms, increasing biological activity and promoting soil health.
Reasons for Biochar Inoculation
Biochar inoculation involves introducing soil conditioners, nutrients, beneficial microorganisms, and organic matter to biochar before it is applied to the soil. Here’s why you might consider inoculating biochar:
- Enhanced Nutrient Availability: Inoculating biochar with nutrients and organic matter ensures that plants have immediate access to essential nutrients. Beneficial microbes help break down these materials, releasing nutrients that are easily absorbed by plants.
- Improved Soil Microbial Diversity: The introduction of beneficial microorganisms increases the diversity of soil microbes. This diversity is crucial for nutrient cycling, disease suppression, and overall soil health.
- Accelerated Plant Growth: Inoculated biochar supports quicker and more robust plant growth. The combination of biochar’s physical properties and microbial activity enhances root development and nutrient uptake.
- Disease Suppression: Certain beneficial microorganisms can protect plants from diseases by outcompeting harmful pathogens, enhancing plant resistance, or producing substances that inhibit disease development.
- Soil Health Restoration: Inoculated biochar is particularly beneficial for degraded soils. The introduction of diverse microbial communities helps restore soil structure and function, revitalizing the ecosystem.
- Enhanced Soil Fertility: By enriching the soil with beneficial microbes and nutrients, inoculated biochar improves soil fertility, leading to healthier plants and higher yields.
Inoculated Biochar: What It Is and Its Benefits
Inoculated biochar is simply biochar treated with beneficial microorganisms or organic amendments before application to the soil. Compared to raw biochar, inoculated biochar offers distinct advantages:
- Immediate Benefits: Microbial activity in inoculated biochar leads to a more immediate improvement in soil health, offering quicker rewards in terms of plant growth and nutrient availability compared to raw biochar.
- Enriched Soil Fertility: Inoculated biochar upgrades the soil’s nutritional profile. The microbes colonizing the biochar facilitate the breakdown of organic matter, enhancing overall soil fertility.
- Sustainable Pest and Disease Management: Beneficial microorganisms in inoculated biochar serve as a natural pest and disease management strategy, reducing reliance on chemical inputs.
- Optimized Soil Functionality: The combination of biochar’s physical properties and the biological activity from inoculation optimizes soil functionality, improving its ability to support healthy plant growth and contribute to environmental sustainability.
- Customizable Applications: Farmers and gardeners can tailor microbial inoculation to suit specific crops or soil conditions. Whether you need nitrogen-fixing bacteria or mycorrhizal fungi, inoculated biochar can be customized to meet diverse agricultural and environmental needs.
Conclusion: Optimized biochar for soil health and plant growth
Understanding the characteristics of raw biochar and the benefit of inoculated biochar is essential for anyone interested in improving soil health. Raw biochar provides a stable carbon source and enhances soil properties, while inoculated biochar takes this a step further by introducing beneficial microorganisms that accelerate nutrient cycling, improve plant growth, and promote soil resilience.
Whether you are a home gardener or a farmer, incorporating biochar into your soil management practices can lead to healthier soil and more productive plants. By choosing the right type of biochar for your needs, you can enjoy the numerous benefits it offers.
Happy gardening and farming!